In today’s fast-paced construction and maintenance industries, mobile scaffolds are imperative in providing safe access to elevated workspaces. Whether you’re considering a career as a scaffold worker or planning to purchase a mobile scaffold for sale, it is essential to understand the training required to operate this equipment safely. This comprehensive guide explores the vital training every mobile scaffold operator must undergo to ensure safety, compliance, and efficiency on the job.
Introduction to Mobile Scaffolds
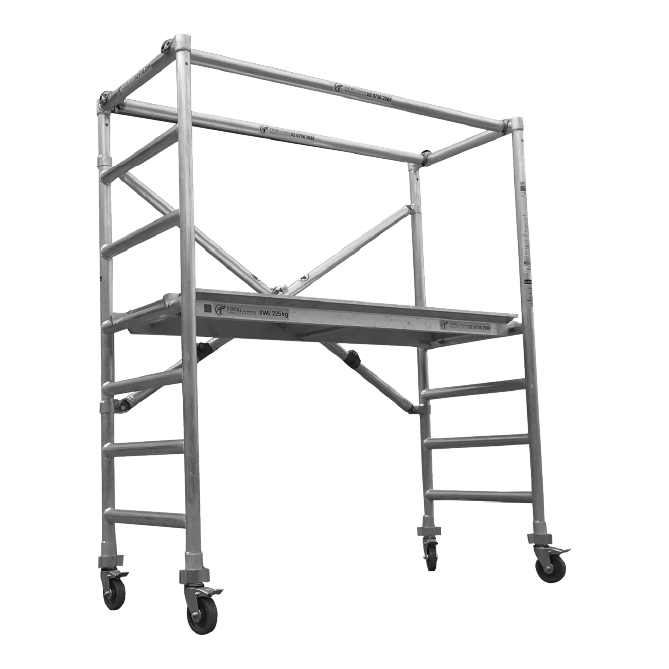
Before delving into the training details, it’s important to understand what mobile scaffolds are and why they are indispensable in the construction industry. Mobile scaffolds are temporary elevated platforms mounted on wheels, allowing easy movement between locations. These structures offer unparalleled flexibility, making them an ideal choice for projects that require frequent repositioning. With various mobile aluminium scaffolds for sale, they have become a staple in many work environments.
Risk Assessment and Hazard Awareness
Identifying Potential Risks
A key component of any mobile scaffold training program is learning to recognise hazards and assess risks. Workers must be trained to evaluate their work surroundings to ensure safe scaffold use. It includes identifying potential electrical hazards, examining ground stability, and accounting for overhead obstructions. The training ensures workers are well-prepared to conduct thorough pre-use inspections, which plays a prominent role in preventing accidents.
Assessing Load Capacities
Understanding the load-bearing limits of a scaffold is critical to preventing structural failure. Scaffold workers must be trained to calculate the combined weight of workers, tools, and materials on the scaffold. They must distinguish between uniformly distributed loads and point loads, and how these can impact scaffolding stability. Additionally, operators must understand the scaffolding’s maximum height and how it affects load capacities and base dimensions.
Assembly and Disassembly Procedures
Correct Assembly Techniques
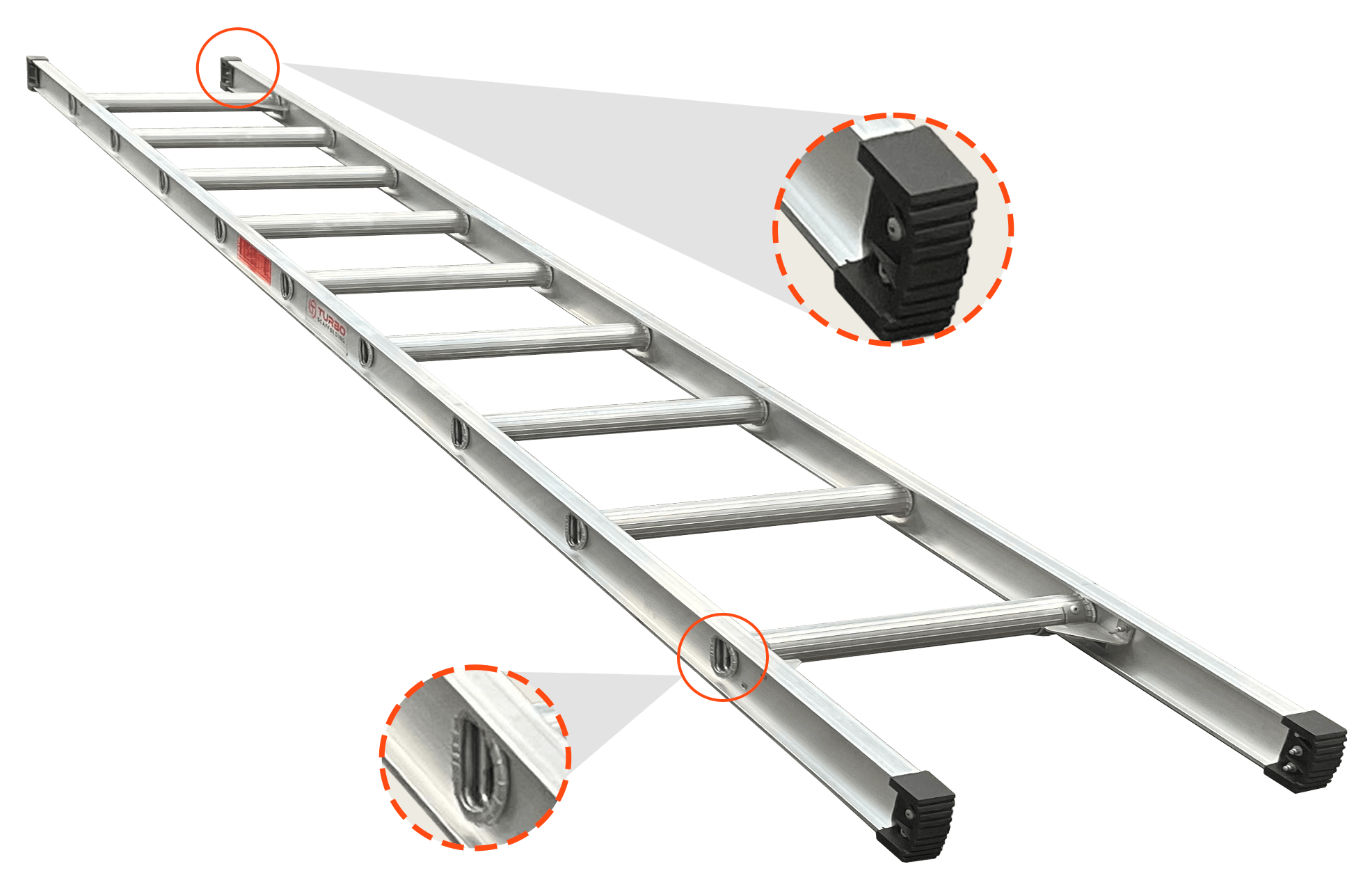
Properly assembling a mobile scaffold is crucial for ensuring safety on site. Workers must be trained in selecting the correct scaffold components, following manufacturer instructions, and ensuring that all parts, such as guardrails and bracing, are correctly installed. The importance of having level and plumb scaffold structures cannot be overstated, as this is vital to the scaffold’s stability.
Safe Disassembly Practices
Equally important is training workers in safe scaffold disassembly procedures. It includes taking apart the scaffold while maintaining safety standards, handling components carefully, and ensuring they are stored for future use properly. Knowing how to safely lower materials during disassembly is another essential skill that reduces the risk of injury.
Mobility and Stability: Key Considerations
Utilising Wheel Lock Mechanisms
Mobile scaffolds are designed for ease of movement, but this also introduces potential hazards. Training on how to use wheel locks properly is a must for workers to ensure stability while the scaffold is in use. Additionally, operators must be taught safe practices for relocating mobile scaffolds, as improper handling can lead to accidents.
Handling Wind Loads and Environmental Factors
Scaffolds are exposed to environmental forces, particularly wind, which can compromise their stability. Workers must be trained to recognise wind speed limits for safe scaffold operation. They should also learn how to secure mobile scaffolds using tie-ins, outriggers, or other methods to prevent them from tipping over in high winds.
Fall Protection and Personal Safety Gear
Using Fall Arrest Systems
While mobile scaffolds come equipped with guardrails as a primary fall protection measure, additional safety precautions are sometimes necessary. Workers must be trained in the proper use of personal fall arrest systems. This training should cover how to fit harnesses correctly, identify secure anchor points, and inspect equipment before use to ensure effectiveness.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Mobile scaffold operators must be trained for essential personal protective equipment (PPE) use. This includes hard hats, safety goggles, steel-toed boots, and high-visibility clothing. Training should also cover checking PPE for wear and tear to maintain safety standards on-site.
Inspection and Maintenance Protocols
Daily Scaffold Inspections
Regular inspections are vital to ensuring the safety of mobile scaffolds. Workers should be trained to perform daily inspections, looking for structural integrity, proper guardrails, and secure connections. They must also check for any signs of wear or damage to components that could compromise safety.
Ongoing Maintenance Requirements
Maintaining a mobile scaffold is essential for extending its lifespan and ensuring safety. Training programs must teach workers how to clean scaffold components, lubricate moving parts, and store them correctly to prevent deterioration. Knowing when to replace worn or damaged components is crucial for avoiding accidents.
Legal Compliance and Industry Standards
Understanding Safety Standards
Mobile scaffold operators must be familiar with the safety standards that govern scaffold use. In Australia, these standards are set out in the ‘Australian Standard for Scaffolding (AS/NZS 1576)’ and the ‘AS/NZS 4576’. Training programs must ensure workers understand these regulations, as well as any local or site-specific requirements that apply to scaffold use.
Record-Keeping and Documentation
Maintaining accurate records is essential for compliance with safety regulations. Scaffold workers must be trained in keeping detailed inspection logs, documenting maintenance activities, and recording their training certifications. This not only ensures compliance but also helps create a safer work environment by keeping track of scaffold conditions.
Practical Training and Emergency Response
Hands-On Scaffold Training
Effective training programs must include practical, hands-on components where workers can apply what they have learned in controlled environments. It allows them to practice scaffold assembly and disassembly, conduct inspections, and perform risk assessments, all under the guidance of experienced instructors.
Emergency Procedures and Rescue Training
Workers should receive training in emergency response procedures apart from scaffold-specific training. It includes first aid basics, evacuation plans, and rescue techniques for individuals who may have fallen from a height. Proper training in emergency procedures ensures that workers are prepared for any situation.
Wrapping It Up
Proper training is essential for mobile scaffold operators to ensure their safety and the safety of others on the job site. Whether you’re considering purchasing a mobile scaffold for sale or planning to improve your team’s skills, investing in comprehensive training will yield long-term benefits. From understanding scaffolding maximum height to mastering fall protection measures, well-trained operators are the cornerstone of any successful scaffolding operation.
For more details on safe scaffold use, please refer to our complete guide for mobile scaffolds.